A digital haptic implementation know-how that permits all customers to expertise the identical tactile sensation has been developed. A analysis staff led by Professor Park Jang-Ung from the Heart for Nanomedicine throughout the Institute for Fundamental Science (IBS) and Professor Jung Hyun Ho from Severance Hospital’s Division of Neurosurgery has developed a know-how that gives constant tactile sensations on shows.
This analysis was performed in collaboration with colleagues from Yonsei College Severance Hospital. It was revealed in Nature Communications on August 21, 2024.
Digital haptic implementation know-how, also called tactile rendering know-how, refers back to the strategies and methods that simulate the sense of contact in a digital surroundings. This know-how goals to create the feeling of bodily contact with digital objects, enabling customers to really feel textures, shapes, and forces as in the event that they had been interacting with real-world objects, though the objects are digital.
The know-how is seeing growing makes use of within the realms of digital actuality (VR) and augmented actuality (AR), the place it’s used alongside visible and auditory cues to bridge the hole between the digital and bodily worlds.
Notably, electrotactile methods, which generate tactile sensations by electrical stimulation fairly than bodily vibrations, are rising as promising next-generation tactile rendering applied sciences. The feeling of contact is mediated by mechanoreceptors, that are tactile sensory cells situated within the pores and skin that transmit tactile data to the mind within the type of electrical alerts.
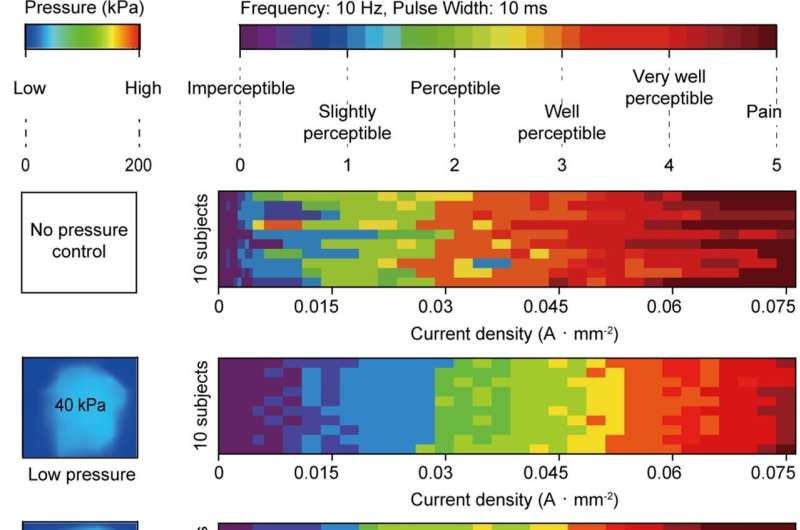
Electrotactile methods artificially generate these electrical alerts, thereby simulating the sense of contact. Exact and diverse tactile experiences could be created by adjusting present density and frequency.
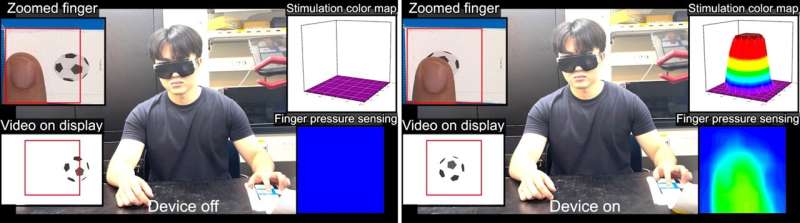
Regardless of their potential, present electrotactile applied sciences face challenges, significantly in security and consistency. Variations in pores and skin contact stress can result in unstable tactile sensations, and the usage of excessive currents raises security considerations. To deal with these points, the IBS analysis staff developed a clear pressure-calibratable interference electrotactile actuator (TPIEA).
TPIEA contains two important elements: an electrode part accountable for producing electrotactile sensations and a stress sensor part that adjusts for finger stress. Researchers tremendously lowered the impedance of the electrode by making use of platinum nanoparticles to an indium tin oxide-based electrode.
This not solely decreased impedance in comparison with standard electrodes but additionally achieved a excessive transmittance of roughly 90%. The built-in stress sensor ensures that customers expertise constant tactile suggestions no matter how they contact the show.
As well as, the analysis staff performed a somatosensory evoked potential (SEP) check to quantify tactile sensations. By analyzing the responses of the consumer’s somatosensory system to variations within the present and frequency of electrotactile stimulation, they had been capable of quantitatively differentiate and standardize tactile sensations.
The staff efficiently carried out greater than 9 distinct sorts of electrotactile sensations, starting from these resembling hair to these resembling glass, relying on the present density and frequency of the electrical stimulation. The staff additional demonstrated that the TPIEA could possibly be built-in with smartphone shows to reliably produce advanced tactile patterns.
Moreover, the analysis launched interference phenomena into the realm of electrotactile know-how. The interference phenomenon pertains to the alterations in frequency and amplitude that happen when two electromagnetic fields overlap.
This allowed the researchers to elicit the identical depth of electrotactile sensation with a present density that’s 30% decrease than beforehand required and to attain an approximate 32% enhancement in tactile decision. This analysis demonstrates the very best stage of tactile decision amongst present electrotactile applied sciences, together with the Teslasuit.
Lead researcher Park Jang-Ung remarked, “By this electrotactile know-how, we will successfully combine visible data from shows with tactile data. We anticipate that the findings of this analysis will considerably improve the interplay between customers and units throughout numerous AR, VR, and sensible machine functions primarily based on interference stimulation.”
Extra data:
Kyeonghee Lim et al, Interference haptic stimulation and constant quantitative tactility in clear electrotactile display with pressure-sensitive transistors, Nature Communications (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-51593-2
Quotation:
Improved digital haptic know-how permits uniform tactile sensation throughout shows (2024, September 9)
retrieved 11 September 2024
from https://techxplore.com/information/2024-09-virtual-haptic-technology-enables-uniform.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.



