Lately, engineers and materials scientists have launched more and more versatile electronics that could possibly be used to create new wearable gadgets, reminiscent of good watches, biosensors and health-monitoring applied sciences. To be safely worn by people for extended intervals of time, these electronics must also be permeable (i.e., letting air and humidity cross by way of) and bio-compatible (i.e., not dangerous to the human physique).
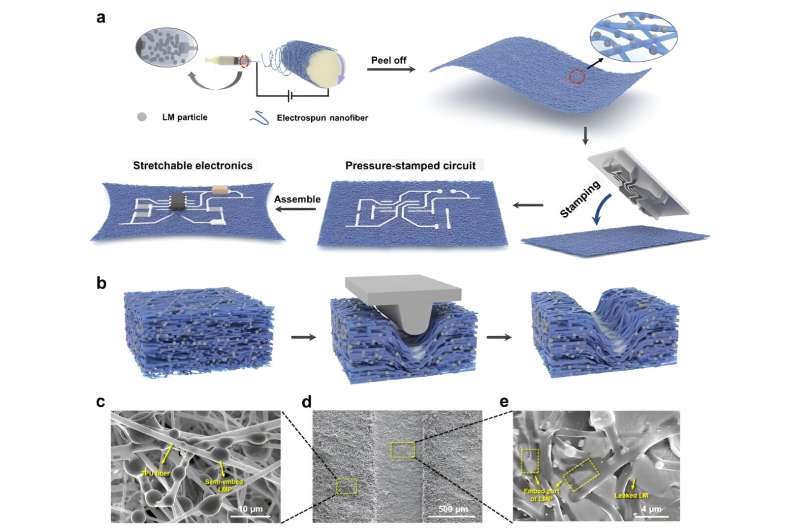
Researchers at Soochow College in China not too long ago launched a brand new methodology to manufacture liquid steel-based stretchable electronics which are stretchable, breathable and bio-compatible. Their proposed technique, outlined in a paper in Nature Electronics, entails using circuit-patterned stamps to create multi-functional versatile digital parts for wearable gadgets.
“Liquid metal-based stretchable electronics have garnered substantial curiosity in latest instances, owing to their promising prospects within the realm of wearable electronics,” Feng Yan, co-author of the paper, informed Tech Xplore.
“However, urgent challenges persist, together with intricate fabrication processes encompassing etching and oxygen-plasma remedy, together with suboptimal interface interactions between liquid steel and polymeric substrates, leading to compromised cyclic tensile stability.”
Liquid metal-based stretchable digital supplies usually include varied limitations, which stop or restrict their potential for creating personalised and customised circuits. As a part of their latest research, Yan and his colleagues got down to tackle and overcome these limitations, by introducing another methodology for fabricating liquid metal-based versatile electronics.
“Our methodology entails a mix of electrostatic spinning and pressure-stamping, which bridges the technical hole between breathability, precision and processability in stretchable digital gadgets,” Yan defined. “The semi-embedded liquid steel particles inside nanofibers can rupture beneath strain, and spill over to type steady liquid steel areas, enabling the selective development of conductive pathways with excessive circuit accuracy and excellent stability.”
Utilizing their newly-devised methodology, the researchers have been capable of quickly put together breathable and stretchable circuits. The fabricated circuits exhibited a excessive decision (i.e., minimal linewidths of fifty µm) and a excessive stability, operating for over 30,000 cycles beneath a pressure of 100%.
When built-in with completely different digital parts, the pressure-stamped electronics created by Yan and his colleagues have been discovered to assist completely different capabilities, together with sq. wave sign outputs, gentle emission and wi-fi charging. Which means they could possibly be extremely versatile parts for wearable gadgets, permitting engineers to make use of the circuits to understand completely different desired capabilities.
“The outstanding biocompatibility and permeability of the circuits we created make them well-suited for accumulating bioelectrical indicators,” Yan mentioned. “Moreover, its recycling capability and universality spotlight its broad potential within the realm of versatile electronics.”
Yan and his colleagues have already used their stretchable circuits to create prototype sensors for monitoring bioelectrical indicators. Sooner or later, they could possibly be built-in into different wearable gadgets for particular medical or sports-related purposes.
An additional benefit of the group’s versatile digital circuits is that the liquid metal-containing membranes they’re based mostly on can simply be dismantled into particular person parts and recycled. This might considerably scale back their hostile impression on the atmosphere, which may additionally contribute to their large-scale deployment.
“We now plan to understand the preparation of multilayer circuit boards with interlayer interconnections,” Yan added. “By exactly modulating the modulus and dimension of liquid metals and nanofibers, we additionally aspire to empower the circuits with the potential to be activated in distinct layers, tailor-made exactly to our evolving necessities.”
Extra data:
Sijie Zheng et al, Strain-stamped stretchable electronics utilizing a nanofibre membrane containing semi-embedded liquid steel particles, Nature Electronics (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41928-024-01194-0
© 2024 Science X Community
Quotation:
A brand new technique to manufacture stretchable and breathable electronics (2024, July 18)
retrieved 19 July 2024
from https://techxplore.com/information/2024-07-method-fabricate-stretchable-breathable-electronics.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.



