Some components of the world have been so worthwhile in making low cost renewable electrical power that we frequently have an extreme quantity of of it. One doable use for that low-cost energy: Altering carbon dioxide into fuel and completely different merchandise using a device referred to as a membrane-electrode assembly.
A workforce of scientists from Lawrence Berkeley Nationwide Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) and the School of California Berkeley have developed a model new technique to understanding this promising experience by means of physics modeling. The paper, which was printed throughout the journal Nature Chemical Engineering, may help scientists uncover methods to reinforce membrane-electrode assembly effectivity.
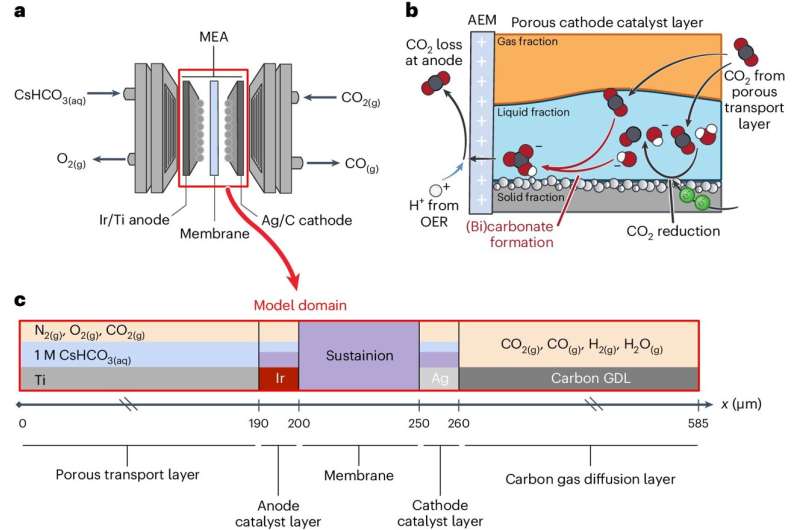
Carbon dioxide is likely to be transformed into worthwhile feedstocks harking back to carbon monoxide and ethylene, which producers use to make merchandise along with chemical substances and packaging. A method to try this is with membrane-electrode assemblies, which might be items that embody two electrodes separated by a membrane.
Moreover utilized in fuel cells that flip inputs like hydrogen into electrical power, membrane-electrode assemblies keep promise for being able to make use of surplus renewable power to run response sequences that catalyze carbon dioxide into completely different chemical substances. Nonetheless these items have points with effectivity, and their workings are normally not however completely understood.
“Membrane-electrode assemblies are troublesome packages with a variety of layers. Each layer holds completely completely different chemical species, parts, and particles,” said Adam Weber, a senior scientist at Berkeley Lab and corresponding creator of the study.
“Often, we don’t truly know why experiments with membrane-electrode assemblies produce certain merchandise, or why they fail to remodel an even bigger proportion of a given amount of carbon dioxide.”

Laptop modeling can help predict which gadget parameters will produce the easiest outcomes, nevertheless they’re normally a lot much less right at anticipating factors harking back to crossover, which is when carbon dioxide strikes all through the membrane instead of reacting. To boost model accuracy, the researchers turned to Marcus–Hush–Chidsey kinetics, an idea that beforehand had not been built-in into membrane-electrode assembly modeling and is confirmed to be important for understanding the response mechanism.
The researchers validated their model in opposition to experimental data, discovering that it did a higher job of predicting real-world outcomes than earlier fashions. Amongst completely different advantages, the utilization of Marcus–Hush–Chidsey kinetics made it doable to account for the place of water orientation.
The workforce then ran digital experiments with its model to find how completely completely different membrane-electrode assembly designs carried out relating to carbon-dioxide utilization and selectivity for desired merchandise. “With this work, now we’ve got confirmed how one can leverage chemical engineering concepts in direction of these superior utilized sciences which may be coming on-line,” he said. “That provides us insights and ideas for optimizing these cell designs and provides so we’ll go forward and make them.”
A number of of the variables the workforce examined almost included catalyst-layer thickness and catalyst-specific ground house. As well as they uncovered design tips throughout the importance of coupled ion and water transport, along with tradeoffs between transport phenomena and response and buffer kinetics. All of these change the final energy effectivity, merchandise obtained, and amount of carbon dioxide remodeled.
“Having a digital twin of a system enables you to probe a loads larger parameter home far more shortly than in experiments, which might be generally superior and require explicit instruments,” Weber said, together with, “We is not going to see the place every molecule is in an experiment. Nonetheless in a model, we’ll.”
Weber said the following step throughout the evaluation is to increase the model’s complexity to have the flexibility to take a look at effectivity over a membrane-electrode assembly’s lifetime, amongst completely different variables.
Further data:
Eric W. Lees et al, Exploring CO2 low cost and crossover in membrane electrode assemblies, Nature Chemical Engineering (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s44286-024-00062-0
Citation:
A higher model for altering carbon dioxide into fuels and merchandise (2024, June 3)
retrieved 3 June 2024
from https://techxplore.com/data/2024-06-carbon-dioxide-fuels-products.html
This doc is subject to copyright. Apart from any truthful dealing for the goal of private study or evaluation, no
half is also reproduced with out the written permission. The content material materials is provided for information features solely.


