Digital waste, or e-waste, is a quickly rising international downside, and it is anticipated to worsen with the manufacturing of latest sorts of versatile electronics for robotics, wearable gadgets, well being displays, and different new purposes, together with single-use gadgets.
A brand new form of versatile substrate materials developed at MIT, the College of Utah, and Meta has the potential to allow not solely the recycling of supplies and elements on the finish of a tool’s helpful life, but additionally the scalable manufacture of extra advanced multilayered circuits than present substrates present.
The event of this new materials is described this week within the journal RSC: Utilized Polymers, in a paper by MIT Professor Thomas J. Wallin, College of Utah Professor Chen Wang, and 7 others.
“We acknowledge that digital waste is an ongoing international disaster that is solely going to worsen as we proceed to construct extra gadgets for the web of issues, and as the remainder of the world develops,” says Wallin, an assistant professor in MIT’s Division of Supplies Science and Engineering. Thus far, a lot educational analysis on this entrance has aimed toward creating alternate options to standard substrates for versatile electronics, which primarily use a polymer known as Kapton, a commerce identify for polyimide.
Most such analysis has targeted on completely completely different polymer supplies, however “that actually ignores the industrial facet of it, as to why individuals selected the supplies they did to start with,” Wallin says. Kapton has many benefits, together with wonderful thermal and insulating properties and prepared availability of supply supplies.
The polyimide enterprise is projected to be a $4 billion international market by 2030. “It is all over the place, in each digital machine principally,” together with components such because the versatile cables that interconnect completely different elements inside your cellphone or laptop computer, Wang explains. It is also extensively utilized in aerospace purposes due to its excessive warmth tolerance. “It is a basic materials, however it has not been up to date for 3 or 4 a long time,” he says.
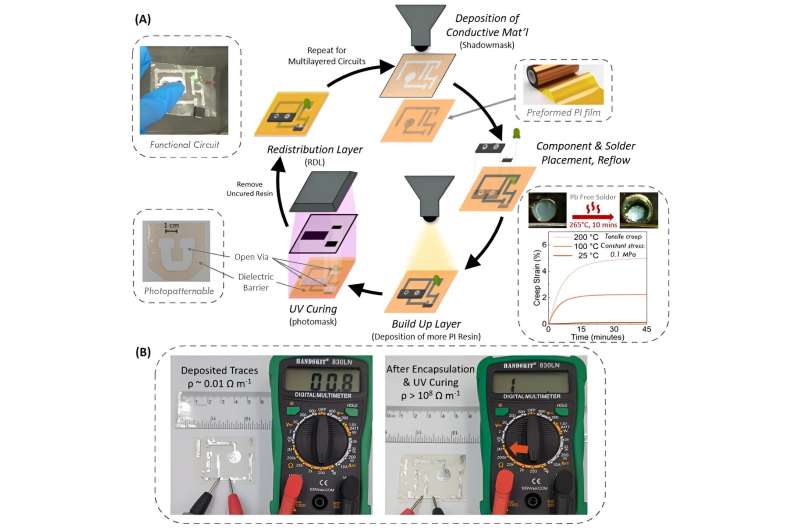
Nevertheless, it is also just about unattainable to soften or dissolve Kapton, so it might probably’t be reprocessed. The identical properties additionally make it more durable to fabricate the circuits into superior architectures, corresponding to multilayered electronics. The standard method of constructing Kapton includes heating the fabric to wherever from 200°C to 300°C. “It is a moderately sluggish course of. It takes hours,” Wang says.
The choice materials that the crew developed, which is itself a type of polyimide and due to this fact ought to be simply appropriate with present manufacturing infrastructure, is a light-cured polymer just like these now utilized by dentists to create robust, sturdy fillings that treatment in just a few seconds with ultraviolet gentle. Not solely is that this technique of hardening the fabric comparatively quick, it might probably function at room temperature.
The brand new materials may function the substrate for multilayered circuits, which gives a method of significantly rising the variety of elements that may be packed right into a small type issue.
Beforehand, because the Kapton substrate would not soften simply, the layers needed to be glued collectively, which provides steps and prices to the method. The truth that the brand new materials could be processed at low-temperature whereas additionally hardening in a short time on demand may open up potentialities for brand spanking new multilayer gadgets, Wang says.
As for recyclability, the crew launched subunits into the polymer spine that may be quickly dissolved away by an alcohol and catalyst answer. Then, valuable metals used within the circuits, in addition to total microchips, could be recovered from the answer and reused for brand spanking new gadgets.
“We designed the polymer with ester teams within the spine,” not like conventional Kapton, Wang explains. These ester teams could be simply damaged aside by a reasonably gentle answer that removes the substrate whereas leaving the remainder of the machine unhurt. Wang notes that the College of Utah crew has co-founded an organization to commercialize the expertise.
“We break the polymer again into its authentic small molecules. Then we will accumulate the costly digital elements and reuse them,” Wallin provides. “Everyone knows in regards to the provide chain scarcity with chips and a few supplies. The uncommon earth minerals which can be in these elements are extremely beneficial. And so we expect that there is a large financial incentive now, in addition to an environmental one, to make these processes for the recapture of those elements.”
Extra info:
Caleb Reese et al, Photopatternable, Degradable, and Performant Polyimide Community Substrates for E-Waste Mitigation, RSC Utilized Polymers (2024). DOI: 10.1039/D4LP00182F
This story is republished courtesy of MIT Information (internet.mit.edu/newsoffice/), a well-liked website that covers information about MIT analysis, innovation and educating.
Quotation:
New substrate materials for versatile electronics may assist fight e-waste (2024, August 6)
retrieved 6 August 2024
from https://techxplore.com/information/2024-08-substrate-material-flexible-electronics-combat.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.



