Over the previous few a long time, electronics engineers have developed more and more versatile, versatile and extremely performing gadgets for a variety of real-world purposes. A few of their efforts have been geared toward creating sensible and sensing textiles, which could possibly be used to manufacture stretchy robotic programs, medical gadgets and wearable applied sciences.
Researchers at Jiangnan College not too long ago launched a brand new textile engineering strategy to manufacture woven and comfortable actuators for well being care applied sciences and robotic programs. Their proposed fabrication technique, outlined in a paper in Cell Stories Bodily Science, is each scalable and easily-designable, which might contribute to its future large-scale adoption.
“Standard strategies like 3D printing and elastomer casting didn’t fairly meet the necessity for adaptability and luxury in comfortable robotics and wearable gadgets, significantly when it comes to growing built-in gadgets that aren’t solely versatile and useful but additionally low-cost, simply customizable and scalable,” Dr. Fengxin Solar, corresponding creator of the paper, informed Tech Xplore.
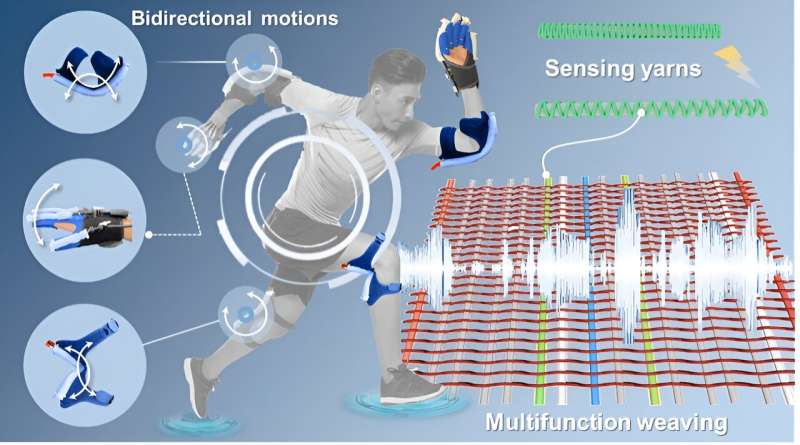
“Impressed by the ‘yarn-to-clothes’ manufacturing technique, we utilized a two-system weaving expertise to seamlessly combine each sensing capabilities and actuation modes into comfortable robotic ‘clothes.'”
The expertise employed by Solar and his colleagues arranges warp and weft yarns (the 2 fundamental parts used to remodel threads into materials) into a transparent planar format whereas weaving them. Because of this it allows the customization of woven actuators, which is attained by rigorously programming the association and composition of yarns.
“Our strategy allows personalised morphing and real-time sensing suggestions, making the woven actuators significantly efficient for purposes like rehabilitation wearables,” Dr. Solar stated. “The fabrication of the sensing yarn is kind of easy, resembling the creation of a braided coiffure. Conductive yarns are braided in a helical sample round stretchy core yarns utilizing an industrial braiding machine, creating pathways for electrical present.”
When the yarn used to weave the actuators is stretched, the pathways by way of which electrical present can circulation are switched off, because of the separation of the conductive yarns’ helices. This variation in construction in flip impacts {the electrical} indicators flowing by way of the yarn, thus enabling the detection of pressure.
“The sensing yarns we developed are built-in straight into the material of our woven actuators,” Dr. Solar stated. “Primarily, because the actuator strikes, the resistance within the yarn adjustments, and this information can be utilized to know how the actuator is performing.”
A singular attribute of the sensing yarns produced utilizing the group’s technique is that they’re totally woven into materials. Because of this they don’t add any weight, stiffness or bulkiness to textiles, permitting actuators to observe their very own actions with out shedding their flexibility and flexibility.
“Because of the two-system weaving expertise, we are able to tailor woven pneumatic actuators to inflate solely in our anticipated instructions, successfully addressing the ‘balloon-like’ inflation downside confronted by the comfortable robotic group,” Dr. Solar stated.
“Furthermore, our weaving technique affords a versatile and scalable resolution for fabricating multi-morphing comfortable actuators, comparable to these able to bilateral bending, twisting and spiraling below a single air provide, by merely adjusting the yarn pressure, density, and woven construction.”
The researchers demonstrated the feasibility of their yarn for growing bilateral bending actuators, which could possibly be used as comfortable robotic grippers. These grippers could possibly be used to imitate the actions of animals, as an illustration reproducing the extension of octopus tentacles to drag objects nearer and grasp them.
“These actuators have additionally sensible purposes in wearable rehabilitation gadgets, the place they’ll present extra exact and adaptive assist to individuals with mobility challenges,” Dr. Solar stated. “The flexibility to program these actuators to imitate pure human actions means they could possibly be utilized in a variety of assistive applied sciences, making them simpler and comfy for customers.”
Sooner or later, the textile engineering strategy launched by this group of researchers could possibly be used to fabricate a variety of versatile parts for medical gadgets and robotic programs. Dr. Solar and his colleagues plan to proceed working in direction of the development of textile manufacturing for technological purposes, devising different weaving and knitting methods.
“We intention to develop textile actuators with improved output and versatile motions in a extra managed manner,” Dr. Solar added. “We consider that refining the design of hierarchical textile constructions will deal with key challenges confronted by the comfortable robotics group, comparable to balancing flexibility and tenacity in comfortable actuators. This course of might develop the potential software of textile-based comfortable robotics and make a better impression on on a regular basis life.”
Extra info:
Haoyun Li et al, Yarn-grouping weaving comfortable robotics with directional inflation, bilateral bending, and self-sensing for healthcare, Cell Stories Bodily Science (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrp.2024.102137
© 2024 Science X Community
Quotation:
Scalable woven actuators provide new potentialities for robotics and wearable gadgets (2024, August 20)
retrieved 4 September 2024
from https://techxplore.com/information/2024-08-scalable-woven-actuators-possibilities-robotics.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.



