Researchers have developed a low-cost, energy-efficient methodology for making supplies that may seize carbon dioxide straight from the air.
Researchers from the College of Cambridge used a technique just like charging a battery to as a substitute cost activated charcoal, which is commonly utilized in family water filters.
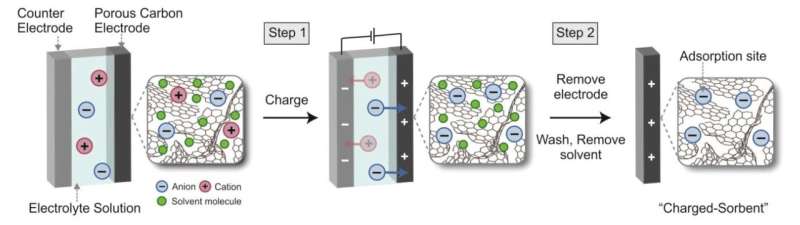
By charging the charcoal ‘sponge’ with ions that kind reversible bonds with CO2, the researchers discovered the charged materials might efficiently seize CO2 straight from the air.
The charged charcoal sponge can be probably extra vitality environment friendly than present carbon seize approaches, because it requires a lot decrease temperatures to take away the captured CO2 so it may be saved. The outcomes are reported within the journal Nature.
“Capturing carbon emissions from the ambiance is a final resort, however given the size of the local weather emergency, it is one thing we have to examine,” stated Dr. Alexander Forse from the Yusuf Hamied Division of Chemistry, who led the analysis.
“The primary and most pressing factor we have to do is scale back carbon emissions worldwide, however greenhouse fuel removing can be regarded as crucial to realize web zero emissions and restrict the worst results of local weather change. Realistically, we have to do every thing we are able to.”
Direct air seize, which makes use of sponge-like supplies to take away carbon dioxide from the ambiance, is one potential method for carbon seize, however present approaches are costly, require excessive temperatures and using pure fuel, and lack stability.
“Some promising work has been accomplished on utilizing porous supplies for carbon seize from the ambiance,” stated Forse. “We needed to see if activated charcoal is likely to be an possibility, because it’s low cost, steady and made at scale.”
Activated charcoal is utilized in many purification purposes, resembling water filters, however usually it may well’t seize and maintain CO2 from the air. Forse and his colleagues proposed that if activated charcoal could possibly be charged, like a battery, it could possibly be an acceptable materials for carbon seize.
When charging a battery, charged ions are inserted into one of many battery’s electrodes. The researchers hypothesized that charging activated charcoal with chemical compounds referred to as hydroxides would make it appropriate for carbon seize, since hydroxides kind reversible bonds with CO2.
The workforce used a battery-like charging course of to cost a reasonable activated charcoal fabric with hydroxide ions. On this course of, the fabric basically acts like an electrode in a battery, and hydroxide ions accumulate within the tiny pores of the charcoal. On the finish of the charging course of, the charcoal is faraway from the “battery,” washed and dried.
Assessments of the charged charcoal sponge confirmed that it might efficiently seize CO2 straight from the air, because of the bonding mechanism of the hydroxides.
“It is a new option to make supplies, utilizing a battery-like course of,” stated Forse. “And the charges of CO2 seize are already similar to incumbent supplies. However what’s much more promising is that this methodology could possibly be far much less energy-intensive, since we do not require excessive temperatures to gather the CO2 and regenerate the charcoal sponge.”
To gather the CO2 from the charcoal so it may be purified and saved, the fabric is heated to reverse the hydroxide-CO2 bonds. In most supplies at present used for CO2 seize from air, the supplies must be heated to temperatures as excessive as 900°C, typically utilizing pure fuel.
Nevertheless, the charged charcoal sponges developed by the Cambridge workforce solely require heating to 90–100°C, temperatures that may be achieved utilizing renewable electrical energy. The supplies are heated by resistive heating, which basically heats them from the within out, making the method sooner and fewer energy-intensive.
The supplies do, nevertheless, have limitations that the researchers are actually engaged on. “We’re working now to extend the amount of carbon dioxide that may be captured, and particularly underneath humid circumstances the place our efficiency decreases,” stated Forse.
The researchers say their method could possibly be helpful in fields past carbon seize, because the pores within the charcoal and the ions inserted into them might be fine-tuned to seize a spread of molecules.
“This method was a sort of loopy thought we got here up with through the COVID-19 lockdowns, so it is at all times thrilling when these concepts really work,” stated Forse. “This method opens a door to creating all types of supplies for various purposes, in a method that is easy and energy-efficient.”
A patent has been filed and the analysis is being commercialized with the help of Cambridge Enterprise, the College’s commercialization arm.
Extra data:
Alexander Forse et al, Capturing carbon dioxide from air with charged-sorbents, Nature (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-07449-2. www.nature.com/articles/s41586-024-07449-2
Quotation:
Scientists develop electrified charcoal ‘sponge’ that may take in CO₂ straight from the air (2024, June 5)
retrieved 5 June 2024
from https://techxplore.com/information/2024-06-scientists-electrified-charcoal-sponge-air.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.



