Electrical autos, large-scale vitality storage, polar analysis and deep area exploration all have positioned increased calls for on the vitality density and low-temperature efficiency of vitality storage batteries. Lately, lithium steel batteries with a excessive particular capability of lithium steel anode have grow to be some of the promising excessive vitality density batteries.
Nonetheless, within the carbonate electrolytes, solvent molecules work together strongly with Li+, which consequently hinders the migration of Li+ and the steadiness of the lithium steel interface. This limitation restricts the applying of lithium steel batteries in low-temperature environments.
A analysis group led by Prof. Li Feng from the Institute of Metallic Analysis of the Chinese language Academy of Sciences has proposed a brand new electrolyte design technique to control the vitality of oxygen bonding within the solvent to attain distinctive efficiency of lithium steel batteries even beneath low-temperature situations.
This work was revealed as a supplementary cowl article in Journal of the American Chemical Society.
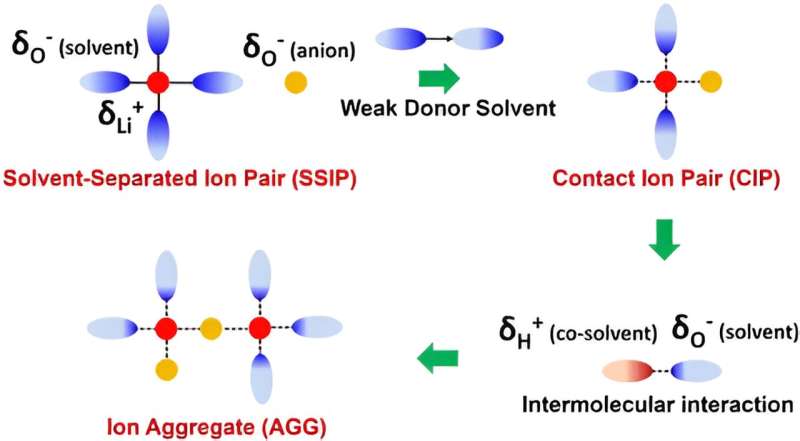
On this examine, the vitality of oxygen bonding within the solvent was discovered to be carefully related to ionic coordination and interfacial transport. The impact of various oxygen bonds, similar to sulfone (S=O), ester (C=O), and ether (C–O) on the construction and temperature adaptability of the electrolyte was elucidated.
By means of intensive screening, tetrahydrofuran-based ether solvents with weak oxygen bonding had been chosen. On this foundation, the interplay between Li+ and solvents was additional attenuated by hydrogen bonding between fluorinated solvent and ether solvent molecules.
This technique considerably accelerates the desolvation technique of Li+ and reduces the unintended effects of solvents on interfacial transport and stability. The lithium steel batteries exhibited a excessive reversibility with 100% capability retention after 150 cycles at room temperature, -20℃ and -40℃.
This is without doubt one of the most steady low-temperature lithium steel batteries reported within the literature. The sensible Ah-level battery exhibited wonderful efficiency with this new electrolyte, and this technique offers a novel strategy to the event of electrolytes for low-temperature batteries.
Extra data:
Nan Piao et al, Designing Temperature-Insensitive Solvated Electrolytes for Low-Temperature Lithium Metallic Batteries, Journal of the American Chemical Society (2024). DOI: 10.1021/jacs.4c01735
Quotation:
Scientists develop new electrolytes for low-temperature lithium steel batteries (2024, July 2)
retrieved 2 July 2024
from https://techxplore.com/information/2024-07-scientists-electrolytes-temperature-lithium-metal.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.



